| Document number | Revision |
|---|---|
| DOCU12213 | 1 |
File storage security
File storage securityOverviewSecurity considerationsWebDAV root folderFiles ShareFiles root folderWorkspaceDocument type foldersDocument all revisions folderDocument single revision folderWorking stateFrozen stateReview stateApproval stateApproved state
Overview
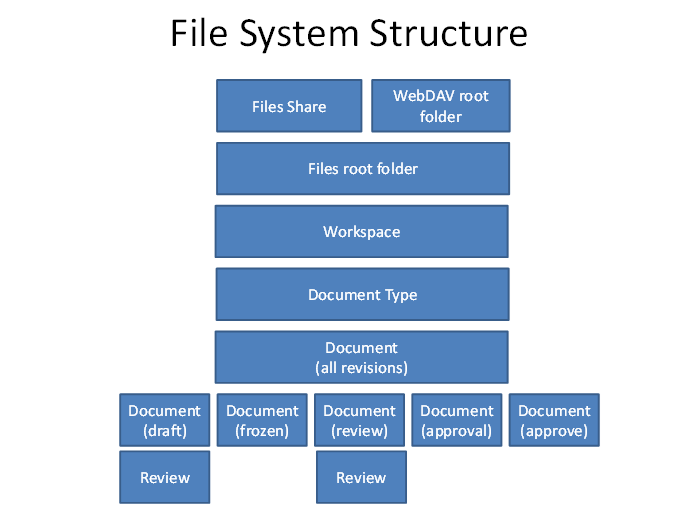
Security considerations
Parameter DefaultTrustees defines user group that by default have read permission to all documents, unless workspace Trustees overrules this. Workspace that is confidential must specify Trustees; otherwise DefaultTrustees will be used as Trustees for Workspace.
Even though a user may not have access to a workspace, a document within the workspace will be visible to the user if the user is document Author, Reviewer, Approver, or if user is on CopyTo distribution list. If the document is in working state and user is document author then user will also have write permission to the document folder.
DefaultTrustees is normally all employees in the company, which is a subset of LdapUserGroups. LdapUserGroups includes all users. In addition to employees LdapUserGroups may include external users, for example consultants, customers and suppliers.
TS controls all security, which is applied automatically. At the time of initial server setup and when IT personal makes changes to server/infrastructure that requires reapplying all file storage security, this may be done from the TS menu System/Security/FileSystem/Apply all.
WebDAV root folder
All users requires read permissions to this folder due to behavior of Microsoft WebDAV client. Microsoft WebDAV client may to be able to connect if user does not have read permissions to WebDAV root folder.
Files Share
Highstage requires the following permission setup:
| Name | Recommended Permissions | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| SYSTEM | Full control | |
| Administrators | Full control | |
| <TS_Refinery user> | Full control | |
| <users> | Change (/Read) | Change (/read) provides users required permissions, but no permissions to change permissions or owner of directories and files which may cause problems. In some situation Everyone may be used. The Everyone group includes all members of the Domain Users, Authenticated Users group as well as the built-in Guest account, and several other Built-in security identifiers like SERVICE, LOCAL_SERVICE, NETWORK_SERVICE, etc. |
The following is general information about Windows shares permissions:
Shares are administered through the MMC, My Computer or through Windows Explorer and permissions can be set on a share in the "Share Permissions" tab. Share level permissions only apply when a file or folder is being accessed via the network and do not apply to a user logged into the machine locally except if using the share path and not a local path. The following are the different share-level permissions:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Read | View folder names and attributes; view file names and attributes; view file data; execute applications. No changes can be made. |
| Change | View, create, delete or change folders, folder names and attributes (except permissions); view, create, delete or change files, file names and attributes (except permissions); view, create, delete or change file data; execute applications. |
| Full control | Can perform any and all functions on all files and folders within the share. |
The Deny permission can also be applied to shares. The Deny permission overrides all others. When folders on NTFS volumes are shared, the effective permission of the user will be the most restrictive of the NTFS and share permissions.
Why users should have Change and not Full control:
You would like to change the default owner assigned to all new files and folders on NTFS file shares to be the Local Administrators group. Thus, preventing users from intentionally modifying permissions on files and folders they create. By default the following rules determine which user or group is assigned owner of the object on Windows Servers.
- If the user is a member of the Local Administrators group then the Local Administrators group is assigned as the owner.
- If the user is not a member of the Local Administrators group then the user is assigned as the owner.
On Windows desktop operating systems (XP, Win7, etc), then all users are treated the same and assigned as owners to all objects they create.
In file sharing, the ability of the owner of an object to change permissions on files and folders can be limited by the permissions set on the share itself. By limiting normal users to only Change on the share you can essentially restrict all normal users to the NTFS Modify permission, thus preventing users from being able modify file and folder permissions even if they are the owner.
Files root folder
The security on this folder is set automatically. IT personal should not set permission on this folder since it may introduce a security issue or cause system exceptions.
TS automatically disable inheritance from WebDAV folder and apply the following permissions:
| Name | Recommended Permissions | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| SYSTEM | Full control | Value of parameter SystemAccounts |
| Administrators | Full control | Value of parameter SystemAccounts |
| <default trustees> | Full control | Value of parameter DefaultTrustees. |
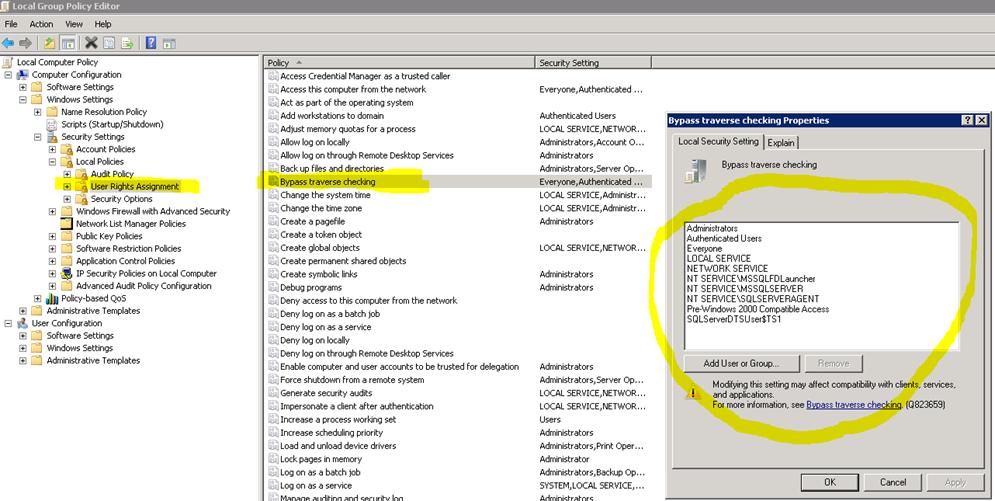
A user may just have permissions to specific document directory where the user is author, reviewer or approver. It is important that users are allowed to traverse parent directories even if the user does not have any permissions to parent directories. This permission is defined by Windows policy “Bypass traverse checking”.
The following is general information about Windows policy “Bypass traverse checking”.
This Windows policy setting “Bypass traverse checking” determines which users can pass through folders without being checked for the special access permission "Traverse Folder" when they navigate an object path in the NTFS file system or in the registry. This user right does not allow the user to list the contents of a folder. It only allows the user to traverse folders.
The default configuration for the Bypass traverse checking setting is to allow all users, including the Everyone group, to bypass traverse checking. Permissions to files and folders are controlled though appropriate configuration of file system access control lists (ACLs) because the ability to traverse the folder does not provide any read or write permissions to the user.
Check the Group Policy Setting (or the local policy setting using gpedit.msc if not in a domain):
Computer Configuration [Policies - this level is present only on Windows Server 2008) Windows Settings Security Settings Local Policies User Rights Assignment Bypass traverse checking
This user right is defined in the Default Domain Controller Group Policy object (GPO) and in the local security policy of workstations and servers:
Workspace
The security on these folder are set automatically. IT personal should not set permission on these folders since it may introduce a security issue or cause system exceptions.
TS apply security disable inheritance from Files root folder and apply the following permissions to this level, and all sub-directories and files:
| Name | Recommended Permissions | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| SYSTEM | Full control | Value of parameter SystemAccounts |
| Administrators | Full control | Value of parameter SystemAccounts |
| <Workspace trustees> | Full control | Value of workspace Trustees column. |
Document type folders
Each document type contained in a workspace has a separate folder. All document type folders inherits permission settings from parent folder (Workspace).
Document all revisions folder
Each document has a folder containing all revisions of the document. All these folders inherit permissions set on parent folder.
Document single revision folder
Permissions will be inherited from Workspace folder with the addition of permissions set on document revision folder according to document state and resources: Author, Reviewers, Approvers and CopyTo distribution list.
TS will apply these permissions automatically.
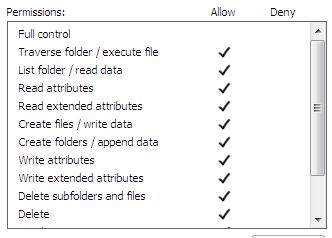
Working state
In working state all authors will have the following NTFS file system permissions:
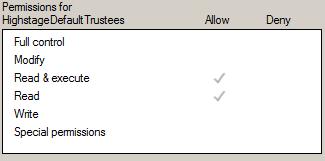
All other users with read permission will have the following NTFS file system permissions:
Observe the following behavior of Windows Shares and NTFS file system:
If a user copies files and directories to server the owner of these file and directories will be set to user. The owner role then gives the user permission to change owner and permissions on these files and directories. This is not desirable, since the risk is that SYSTEM and Administrators no longer will have access to these files and directories until owner is changed by an Administrator and proper permissions are applied, in addition it may introduce system exceptions and be a security issue. To prohibit the user from changing owner and permissions on files copied to server the Files Share permission for the user must be Change (/Read) and not Full Control. Refer to Files Share.
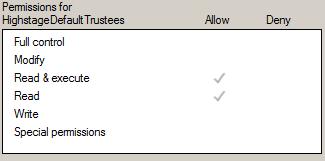
Frozen state
All users with access to the document will have the following NTFS file system permissions:
Review state
All users with access to the document will have the following NTFS file system permissions:

Approval state
All users with access to the document will have the following NTFS file system permissions:

Approved state
All users with access to the document will have the following NTFS file system permissions:

